The role of crankcase ventilation
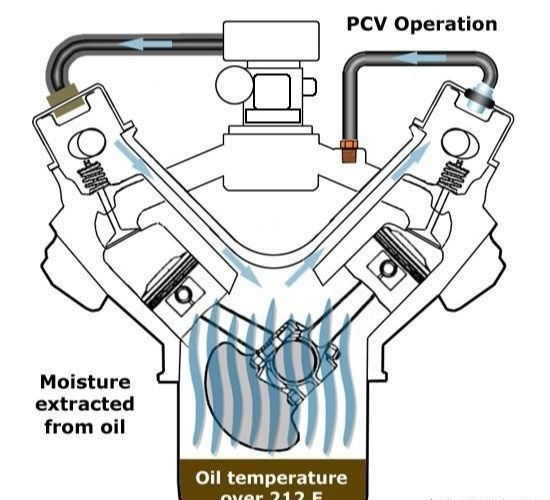
Crankcase ventilation includes natural ventilation and forced ventilation. Modern diesel engines often use forced crankcase ventilation, also known as PCV system.
1. Natural ventilation
Natural ventilation means that a ventilation pipe is arranged on the crankcase and an air filter screen is installed on the pipe. When the pressure in the crankcase increases, the gas leaking into the crankcase is discharged through the vent pipe.
2. Compulsory ventilation
Forced ventilation method, the mixture in the crankcase through the connecting pipe to the appropriate position of the intake pipe, return to the cylinder for re-combustion, which can not only reduce exhaust pollution, but also improve the economy of the engine. Compulsory ventilation is adopted in automobile gasoline engines and gradually in automobile diesel engines. Compulsory ventilation can be divided into open and closed types.
Open forced crankcase ventilation device in the engine at full load and low speed, produced a large volume of air, but the flow control valve opening is reduced, excessive channeling cylinder mixture will be scattered into the atmosphere through the open ventilation cover, the purification rate is only about 75%.
Closed forced crankcase ventilation device can fully control the emission of the crankcase, complete ventilation of the crankcase, prevent the accumulation of sludge and other harmful substances, and reduce the failure and wear of the engine. Closed forced crankcase ventilation device is a necessary design for diesel engine to meet the emission regulations.